AI coding assistants have rapidly surged in popularity between 2024 and 2025, becoming an integral part of daily workflows for development teams. This trend is reflected in the 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey: 76% of respondents said they already use or plan to use AI tools in their development process, and 62% were already using them that same year. A clear sign that AI-powered development is no longer optional — it’s becoming the new stan
But the growing list of tools makes it hard to see which ones actually improve productivity and help you maintain solid code quality. So to help you out, our engineers at Axify tested the leading options to understand which assistants truly reduce friction and speed up delivery.
Here, you’ll compare real tool behavior and see what matters during adoption. You’ll also learn how these tools impact software delivery speed and review cycles. So, let’s start with the basics and look at what an AI coding assistant actually is.
What Is an AI Coding Assistant (or Coding Agent)?
An AI coding assistant (or coding agent) is a tool that supports your work with coding assistance (it generates code). It interprets your natural language prompts and offers you intelligent code suggestions similar to a lightweight pair programmer.
These tools sit in your editor and respond to your intent, whether you’re writing new logic or reviewing past decisions.
And the AI coding market is booming, which shows increased interest and adoption. As such, an analysis of VS Code extensions found 1,085 assistants, with over 90% released in the last two years.
Based on that finding, here’s an industry view worth noting:
“AI has automated all the repetitive, tedious work. The software engineer’s role has already changed dramatically. It’s not about memorizing esoteric syntax anymore.”
- Scott Wu, CEO of Cognition
Now that you have the baseline, read below to see how we evaluated each tool and what actually matters in practice.
Our Evaluation Criteria for Best Coding Agents
At Axify, we tested several AI-powered coding assistants across real projects to see which ones actually help you ship faster. We focused on the same signals we track inside Axify every day.
These include how quickly work moves, how many review cycles a change requires, and how well a tool adapts to your coding style. And because we measure developer performance and collaboration through engineering delivery metrics, we applied that same lens while comparing assistants.
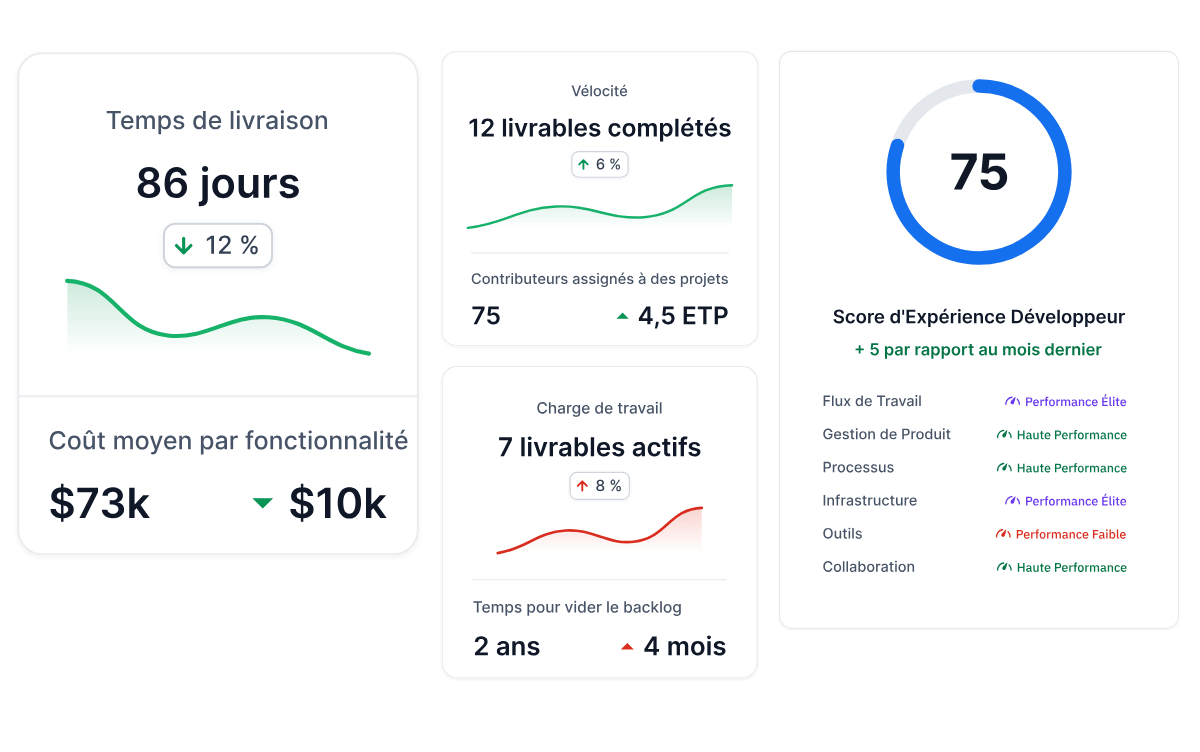
Productivity and Delivery Speed
Speed only matters if it shortens the path from idea to merged change. That’s why we looked at how each assistant handled complex code snippets, how frequently suggestions reduced rework, and whether it supported meaningful progress with a single prompt.
We also checked how assistants behaved in real branches rather than staged examples.
Theoretically, a McKinsey study suggests that writing new code and maintaining it takes far less time when AI is part of the process. This study saw heavy tasks like code refactoring completed in a fraction of the usual effort.
Pro tip: That finding is not always true in practice, though. If you’re wondering how much time AI assistants actually save in real development work, you can read our guide on AI coding time savings for a deeper breakdown.
Code Quality and Verification
Good suggestions are only helpful if they protect standards. That’s why we examined how each assistant treated structure, clarity, and correctness.
We paid close attention to context-aware code suggestions and checked whether they aligned with team conventions. Our team also reviewed how well tools handled unit tests, since teams depend on predictable behavior during change cycles.
And because code quality directly affects stability, we also kept an eye on the two DORA metrics tied to software stability:
- Change Failure Rate (CFR)
- Failed Deployment Recover Time (formerly known as Time to Restore Service; MTTR)
We used these benchmarks as guiding signals: Did the assistant reduce the likelihood of faulty code making it to production? And did it help teams recover faster when issues appeared?
These checks helped us understand whether each assistant supported predictable, low-risk development during change cycles.
Integration and Developer Experience
The best assistants fit into your existing flow. So we evaluated:
- How cleanly each tool connected to your integrated development environment
- How well it handled version control events
- How predictable it felt during long sessions
Smooth integration with development environments mattered just as much as the quality of the suggestions, especially for teams working across multiple editors or languages.
With this out of the way, we'll now move on to the tools themselves so you see where each option stands.
Best AI Coding Assistant Tools [2025 Edition]
The best AI coding assistant tools in 2025 come from GitHub Copilot, Cursor, Qodo, Qwen3 Coder, and Tabnine, among others. This section gives you a clear view of how each one behaves in real work.
Let’s see how they stand out when you want faster coding and stronger support across complex coding queries.
1. GitHub Copilot (Business & Enterprise)

GitHub Copilot is a production-ready AI coding assistant that works directly inside the tools developers already use. Rather than replacing the editor workflow, it enhances it by providing real-time code suggestions, contextual chat, and repository-aware assistance. This allows Copilot to support everything from individual coding tasks to broader, team-level workflows.
Here’s how it works:
Copilot combines inline code completions with a conversational layer that understands your open files, recent changes, and project structure. Developers can:
- Generate code
- Refactor existing logic
- Write tests
- Or explain unfamiliar sections
Of course, you can do all this without leaving the editor.
Another feature we like is that Copilot draws context from the current repository. Therefore, its suggestions tend to align with existing patterns and conventions.
For teams, Copilot Business and Enterprise add governance and security controls that make AI assistance viable at scale. Admins can manage access, enforce usage policies, and reduce the risk of sensitive data exposure. Meanwhile, developers get consistent, low-friction help across daily coding tasks.
Key features:
- Inline code suggestions and multi-line completions inside major IDEs.
- Copilot Chat for explanations, refactoring, test generation, and debugging.
- Context awareness across open files and repository structure.
- Support for a wide range of languages and frameworks.
- Enterprise controls for policy management and secure usage.
Best for: Ideal for teams seeking AI assistance embedded directly into their existing development workflows, without the need to change tools. Based on our evaluation, GitHub Copilot stands out for its strong balance of speed, contextual accuracy, and enterprise readiness.
2. Cursor
Cursor gives you an AI-first coding environment where the assistant sits at the center of your workflow rather than acting as a plug-in on the side. The editor combines writing, refactoring, and debugging with a model-driven layer that reacts to your selections, prompts, and project context.
And because the tool pulls relevant files or functions into each request, it typically produces changes that match your existing patterns without extra guidance. This creates a workflow that feels closer to pair-programming inside the editor rather than switching between windows or chats.
Key features:
- Deep AI integration with in-place code edits.
- Context-aware chat for questions and debugging.
- Strong autocompletion for larger code blocks.
- Lightweight editor with Git and navigation support.
Best for: Developers who want an editor built entirely around AI and prefer a single space for writing, reviewing, and reshaping code. From our testing, this approach feels smooth for rapid iteration and experimentation.
3. Tabnine
Tabnine is a commercial AI coding assistant built around fast, predictable completions and strong editor coverage. It focuses on helping you finish lines and blocks with minimal friction, and it supports cloud, local, and enterprise deployment.
The tool can run on your own infrastructure, and because of that, it might fit teams that want tighter control while still getting precise suggestions. Plus, its enterprise tier adds private models and admin controls, which separate it from lighter, chat-first tools.
Key features:
- Broad language and IDE support across major editors.
- Local and on-prem model options for compliance needs.
- Customization based on internal patterns.
- Multi-line suggestions tuned to project context.
Best for: Teams that want fast, reliable completions with flexible deployment. In our Axify testing, developers liked how Tabnine reduced low-value edits during long sessions without interrupting existing workflows.
4. Gemini Code Assist
Gemini Code Assist gives you Google’s newest model applied directly to real coding tasks. It works across several Google environments, which helps you stay inside the same tools you already use for cloud work, Android development, or notebook experiments.
And since Gemini handles long instructions well, it fits sessions where you need more than quick completions. Its strength shows up when you step beyond simple edits and need guidance that follows the full structure of your project.
Key features:
- Code generation and structured task guidance.
- Explanations for code blocks and debugging steps.
- Integration across Google Cloud and Android tools.
- Support for natural-language instructions.
Best for: Teams already invested in Google Cloud or Android workflows. We tested it and found it helpful for longer tasks that required stable reasoning across several related changes.
5. Sourcegraph Cody
Sourcegraph Cody gives you an assistant that understands your entire codebase instead of just the file you have open. It combines a large model with Sourcegraph’s search index, which helps it pull the right examples and explanations from anywhere in your repository.
And that makes a clear difference in larger projects where context matters as much as the code you are writing. Its value becomes clear when you need answers tied directly to real paths, modules, or historical decisions.
Key features:
- Full-repo awareness through Sourcegraph indexing.
- Natural-language Q&A grounded in actual code.
- Guidance for new implementations and refactors.
- Integrations for web, IDEs, and CLI.
Best for: Teams working in large or complex repositories. During our Axify testing, developers noted how Cody reduced the time spent searching for past decisions or tracking how features were built.
6. JetBrains AI Assistant
JetBrains AI Assistant brings AI support directly into JetBrains IDEs, which keeps your focus in one place instead of switching between tools. It uses project context to guide explanations, generate examples, and help with larger edits.
The tool builds on JetBrains’ analysis engine, so the suggestions tend to fit how your project is structured rather than feeling generic. This makes it useful during review cycles or when working through unfamiliar files.
Key features:
- In-IDE chat for natural-language guidance.
- Code explanations based on selected blocks.
- AI-supported completions and improvement ideas.
- Help with commit messages and refactoring tasks.
Best for: Teams that rely on IntelliJ IDEA, PyCharm, or WebStorm as their main workspace. Our developers at Axify liked how it supported longer reasoning tasks without breaking their flow.
7. CodeGeeX
CodeGeeX is an open-source option built for multilingual code generation and broader flexibility than most commercial assistants. It runs on a 13B-parameter model and supports many programming languages, which helps when you work across different stacks or mixed-language repositories.
And since it can run locally, it fits teams that prefer full control of their environment without sending code outside the organization. Its great when you need a customizable model that adapts to your setup.
Key features:
- Support for 20+ programming languages.
- Local, on-prem, and self-hosted deployment.
- Code-to-code translation across languages.
- VS Code extension and API access.
Best for: Teams that want an open, flexible model without vendor lock-in. At Axify, we noted how CodeGeeX helped with early drafts and translation work across languages without forcing tool changes.
8. Qodo
Qodo is a premium tool with enterprise pricing starting very high (listed at $50K/year for a one-year licence). It serves large engineering teams that need an advanced AI coding agent with strict control over data.
The tool runs in on-prem or private cloud environments. This gives you full ownership of proprietary code and clear boundaries around security and privacy. And because it can be tuned to your internal patterns, suggestions tend to align better with long-term conventions and expectations.
Key features:
- On-prem or private cloud deployment for controlled environments.
- Context-aware suggestions tuned to internal codebases.
- Pull request support with structured improvement hints.
- Integration with enterprise IDEs and broader integrated workflows.
Best for: Large organizations that want an AI partner aligned to strict compliance rules. It fits teams that need deep customization and a controlled data path. Based on our internal Axify testing, engineers found that Qodo holds up well during long refactor phases because its suggestions remain aligned to your codebase’s architecture and standards, even as the code evolves.
9. Qwen3 Coder
Qwen3 Coder is a large-model assistant built for teams that want strong reasoning and clear output across different languages. It uses the Qwen model family, which helps it understand natural prompts and follow longer instructions without losing context.
And because it handles multilingual input well, it fits teams that work across mixed codebases or collaborate in more than one language. Its strength shows up when you need structured help with longer tasks rather than just next-line predictions.
Key features:
- Strong support for many programming languages.
- Multilingual prompt and comment understanding.
- Context-aware generation for complex tasks.
- Clear explanations to help with code comprehension.
Best for: Teams that want a model with broad language support and predictable reasoning. It works well when you handle mixed environments or larger files. Our developers at Axify liked how it stayed consistent during longer sessions that involved several linked changes.
10. Replit Ghostwriter
Replit Ghostwriter is an AI assistant built directly into a cloud IDE, which makes it easy to get real-time help without installing anything locally. It works inside Replit’s browser-based environment, so the assistant always has access to your project context as you write and test code.
The mix of inline suggestions, code transformations, and chat-based guidance creates a smooth workflow for quick experimentation or classroom-style learning. And because everything runs in the cloud, the setup overhead stays low.
Key features:
- Inline completions for faster coding in the editor.
- Chat panel for Q&A, debugging, and guidance.
- Code explanation for breaking down unfamiliar snippets.
- Code transformation for refactoring or rewriting logic.
Best for: Ideal when you want an always-on assistant in a fully hosted IDE. It also suits teams or learners who prototype frequently and want browser-first development. One insight from our engineers is that Ghostwriter shines most when the project stays inside Replit’s ecosystem, where context is consistently available.
11. Figstack
Figstack helps developers understand code faster, especially when dealing with unfamiliar logic. It works as a lightweight assistant that explains functions, analyzes snippets, and converts code across languages.
It was created by Mintlify, and it leans heavily into clarity, documentation, and readability rather than full-scale code generation. So it fits workflows where comprehension matters as much as output.
It also gives developers a quick way to surface intent, complexity, or translation needs without jumping across external tools.
Key features:
- Code explanation for fast comprehension.
- Natural-language Q&A for snippet-level questions.
- Documentation and comment generation.
- Code translation across supported languages.
Best for: Developers who need help understanding existing code or documenting complex sections without slowing down reviews. Our team noticed that Figstack lowers onboarding friction by shortening the time it takes to grasp tricky modules.
Best Free AI Coding Assistants
Free AI tools can support real projects when cost control matters. Free pricing models can also help when you want to test different code generation tools before committing long-term.
And while these options vary in depth, they still give you enough flexibility to evaluate suggestion quality, integration behavior, and the overall impact on your daily workflow.
Free Tools Worth Considering
Free tools can still support meaningful work as long as you understand their limits and strengths. Here are the options that stand out in real projects:
- Pieces for Developers: Is a focused code tool that stores snippets, tracks context, and provides lightweight documentation generation. So it works well when you need quick references or smaller prompts that help you clean up drafts before review.
- Codiga: It adds automated checks driven by static code analysis, which can support teams that want consistent patterns without writing custom lint rules.
- ChatGPT: Remains solid for architectural questions or checking alternative patterns, though it requires careful review due to the lack of real-time repository context.
- GitHub Copilot: Its free tier for students and OSS contributors still offers strong intelligent code completions, though adoption depends on editor compatibility.
- Amazon Q Developer: This tool brings structured assistance with code generation, especially for AWS workflows. It fits teams that want predictable behavior around infrastructure code.
- Warp.dev: It acts more like a browser development environment for terminal workflows, which can help you test commands or scripts with natural prompts.
- Kilo Code: Offers a lightweight set of features built around simple code suggestions. This is ideal for quick prototypes or short experiments.
When Free Tiers Make Sense
Free assistants usually serve as early evaluation tools. They can help you compare suggestion accuracy, editor integration, and overall friction before involving your team.
They also allow you to validate patterns against your preferred code editors without changing your process or exposing private code. Still, these tiers typically cap request volume or limit advanced features.
Next, let's discuss which assistants are easiest for new developers.
Which AI Coding Assistant Is Best for Beginners?
The best AI coding assistant for beginners is the one that guides you through real decisions instead of overwhelming you with options. So the right tool should help you write quality code, correct mistakes, and understand what’s happening behind each suggestion.
It should also feel predictable inside your editor and adapt to everyday habits, even if you’re still learning core concepts. To make this clear, here are the criteria that shape a beginner-friendly experience when working with AI coding agents:
- Ease of setup: Works out of the box with popular IDEs.
- Clear feedback: Suggests readable code and provides deeper code explanation when needed.
- Error handling: Helps fix bugs instead of only generating new snippets.
- Language coverage: Supports common languages such as Python, JavaScript, and Java.
- Learning integration: Surfaces hints, guides, or links to code documentation from inside your editor.
- Cost transparency: Keeps pricing predictable for students or anyone testing tools long-term.
So, here are several assistants that stand out for new developers:
Tabnine
Tabnine gives you simple code completion, which helps you learn patterns without burying you in noise. And because it adjusts to your coding style, it becomes easier to follow your own logic while you grow your skills.
Setup is quick since it works cleanly in VS Code and JetBrains tools. Its small footprint and predictable interface make it a steady starting point when you want accurate code suggestions without large distractions.
Replit Ghostwriter
Ghostwriter works inside the Replit browser development environment, which means there’s nothing to configure. It’s ideal for experiments, school projects, or hobby coding because suggestions appear inside a workspace that already handles files, tests, and sharing.
It also produces clear explanations next to the output, which can help you understand the reasoning. That can speed up early problem-solving, especially when you’re learning how tools behave under complex coding tasks.
JetBrains AI Assistant
This assistant fits developers who use IntelliJ, PyCharm, or WebStorm as their main environment. It provides structured guidance, inline notes, and suggestions that help you understand project structure.
So it’s helpful when you want support during reviews or want to check how a piece of logic connects to another part of your project. Its suggestions remain grounded in your files, which helps you maintain code compliance across larger codebases.
Gemini Code Assist (Google)
Gemini Code Assist feels suited for training and practice because it focuses on clarity. It offers step-by-step help, supports efficient code generation, and includes dedicated modes for fixing errors.
And when you need help rewriting something or comparing alternatives, its detailed explanations act like a slow, steady guide. Instead of generating unclear or overly aggressive changes, it guides you through step-by-step decisions.
Pro tip: Thinking about how AI reshapes software development beyond individual tools? Take a look at our guide on AI’s impact on software engineering for a strategic view.
Which AI Coding Assistant Will You Pick?
The best AI coding assistant for you is the one that improves real delivery work rather than offering surface-level help. So the right choice depends on how well a tool supports your flow, adapts to your habits, and provides smarter code suggestions that hold up during review.
And this is where Axify steps in.
Our platform measures the true impact of these assistants by tracking cycle time, review patterns, and how each suggestion shapes your entire coding process. That gives you a clearer view of where the gains actually come from.
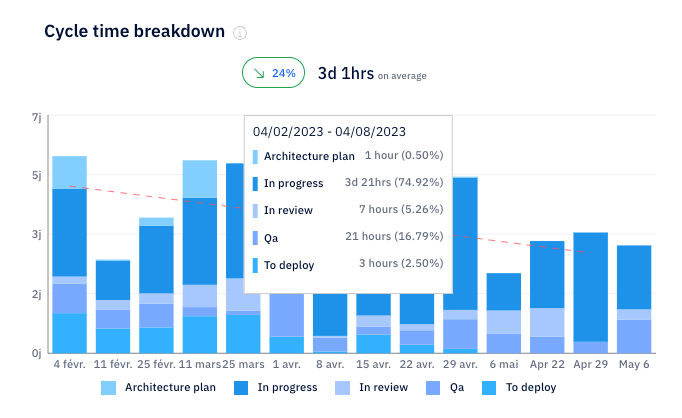
With this in mind, reach out to us today if you want help picking the right tool for your team.






.png?width=60&name=About%20Us%20-%20Axify%20(2).png)


