Fast-moving markets reward teams that release updates quickly and with precision. Yet pushing changes too fast without reliable automation can increase the risk of downtime and erode confidence across your engineering and product teams.
That’s why mature organizations embrace continuous deployment — a practice that automatically delivers every validated change to production, ensuring speed without sacrificing stability.
So, to achieve faster delivery, cleaner feedback loops, and measurable improvement across each release, we'll show you how continuous deployment works. You'll also learn which tools support it, and how platforms like Axify help you measure performance.
But first, let’s clarify what continuous deployment really means.
What Is Continuous Deployment?
Continuous deployment means every validated change in your codebase moves automatically into production without manual approval. It’s the final stage of a deployment pipeline, where continuous integration verifies the code, and automation handles the release.
This approach keeps your product live and improving, especially for SaaS or web-based systems that rely on frequent updates. That’s because reliable automated testing and monitoring and alerting tools remove the delays and risks tied to manual handoffs.
And the momentum behind this shift keeps accelerating...
According to Market Research Future, global CI/CD tools are expected to grow from $9.41 billion in 2025 to $38.75 billion by 2034 (CAGR 15.19%). This shows how important automation has become for modern delivery pipelines.
“We cannot achieve deployments on-demand if each of our production code deployments take weeks or months … The countermeasure is to automate our deployments as much as possible, with the goal of being completely automated so they can be done self-service by any developer.”
- Gene Kim, Wall Street Journal Bestselling Author
Continuous Deployment Examples
Continuous deployment is meaningful when you see how it reshapes a large organization’s daily operations.
LinkedIn’s transition to automated deployment is a clear example.
Before automation, developers worked in long feature branches, and they merged massive code changes into a single trunk. This created delays, merge conflicts, and frequent regressions.
The shift to a shared Git repository and continuous validation pipeline changed that completely.
Developers began committing smaller, verified updates that passed through an automated testing suite before being automatically deployed to production environments once they met all criteria. This new deployment process shortened feedback loops, reduced risk, and kept the platform improving daily.
These deployments happened many times per day, but that didn’t always mean users immediately saw new features. Deployment is the act of moving code to production, while release is when that code becomes visible or accessible to users.
Pro tip: If you want a deeper look at how deployment connects to release, check out our detailed comparison article.
This automation shortened feedback loops, reduced risk, and kept the platform improving daily. It also showed that automation is about stability and measurable progress. The same principles now guide how most modern software development teams build, deploy, and release updates efficiently.
Next, let’s break down how continuous integration connects to continuous deployment in this delivery flow.
Continuous Integration vs. Continuous Deployment
Continuous integration (CI) focuses on merging small, frequent code updates into a shared source control repository so that issues surface early. Each change triggers automated builds and test runs, which confirm the code is stable and production-ready.
Once CI validates the build, continuous deployment (CD) continues the process by automating delivery into production.
CD applies the same automation principles beyond integration. The point is for every validated build to be deployed to production environments without manual approval. Release management can still remain separate, so your teams control when new features become visible to users.
A typical pipeline follows this flow:
Code commit → automated build → test execution → artifact creation → deployment to staging → verification → automated production release → post-deployment monitoring.
Teams that master this flow remove friction and create measurable speed without compromising reliability.
In practice, teams use a mix of managed and self-hosted CI/CD tools to adapt to different workloads and compliance needs. And it works:
Those who use both managed and self-hosted CI/CD tools tend to outperform those that rely on one form. This shows that integrated tool diversity can strengthen deployment automation and delivery performance.
You can also watch this short interview where an expert explains CI/CD in simple terms and how teams can start automating their deployments:
Next, let’s compare this continuous process with an approach that still includes human approval before release.
Continuous Delivery vs. Continuous Deployment
Continuous delivery automates the release flow up to the production stage, but keeps one final checkpoint, and that's a manual approval before deployment. This approach helps you maintain control, especially if you work in regulated sectors or manage high-risk systems.
Many teams see it as a sweet midpoint between automation and oversight, which is probably why this hybrid model is also gaining commercial traction:
According to Grand View Research, the global continuous delivery market reached about $3.67 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $12.25 billion by 2030.
Continuous deployment, on the other hand, eliminates that manual gate entirely. Once your tests pass, validated builds move directly to production through automated deployments.
This shift demands strong trust in your cloud build configurations, testing coverage, and monitoring tools.
Adoption of both is expanding quickly:
During the CDCon event, 29% of respondents reported active involvement in continuous delivery or deployment. This shows how mainstream these practices have become.
Also, feel free to watch this brief video where Eric Minick from IBM clearly breaks down how continuous delivery and continuous deployment differ in practice:
Up next, let’s look at the measurable business and operational benefits you can expect from continuous deployment.
Benefits of Continuous Deployment
Continuous deployment creates measurable gains for teams that want to ship updates faster without compromising stability. Automating validation and delivery allows you to shorten feedback loops and free engineers from repetitive deployment tasks.
Here are the main advantages you gain when adopting this approach:
- Faster time to market: Every verified build reaches production automatically. This lets new features and software updates reach users in hours instead of weeks because faster release is connected to faster deployments.
- Higher quality through fast feedback loops: Automated pipelines and integrated bug detection tools surface issues early, which cuts rework cycles. This correlation between faster detection and cleaner production outcomes is well-documented. According to research from IT Convergence, organizations using test automation in CI/CD pipelines report 40% faster deployment cycles and 30% fewer post-production defects.
- Reduced manual effort and risk (driving ROI): Automated validation removes human error from deployment scripts and approvals. This operational consistency has clear financial outcomes. CI/CD adopters have reported up to 50% reductions in development and operations costs due to this efficiency.
- Happier developers and customers: Automation gives developers confidence to deploy frequently, recover quickly, and accelerate releases. Meanwhile, users experience fewer interruptions and faster improvements.
- Continuous improvements: With data flowing from production back into your testing environments, every iteration becomes a learning loop. Each cycle strengthens delivery accuracy and improves the overall customer experience.
Together, these benefits make continuous deployment a strategic advantage for your organization. Now, let's see where this approach fits best.
Continuous Deployment Use Cases
Continuous deployment fits best in environments where change happens quickly and where delivery predictability matters. In turn, this allows you to ship improvements as soon as they’re ready for deployment instead of waiting for scheduled release cycles.
SaaS platforms with frequent updates need this.
For subscription-based software, the ability to deliver small, incremental improvements drives retention and reduces churn. Automated pipelines running on Google Cloud or AWS Cloud help teams deploy multiple times per day.
This keeps the platform stable while continuously refining the user experience. When issues surface, Argo CD, Spinnaker, or similar tools enable fast rollbacks with minimal disruption.
Consumer web apps needing fast iteration depend on it.
In competitive markets like eCommerce or social platforms, even short deployment delays can hurt engagement because they lead to release delays. Timely interface changes or personalization updates are typically what keep users active and conversions steady.
Continuous deployment lets your release team push validated features as soon as they’re approved for production. This can be within minutes of validation, which is great because you can align updates with behavioral trends or ongoing campaign timing.
Companies optimizing for developer velocity and fast feedback thrive with it.
Engineering organizations focused on Agile software development benefit most from automated delivery, of which continuous deployment is a part of. Linking builds, testing, and deployment through integrated tools such as GitHub Actions allows teams to shorten the distance between idea and execution.
The faster you can validate changes, the faster you can reallocate engineering effort to high-value work.
Continuous Deployment Disadvantages
Even mature delivery pipelines come with risks, especially when speed and deployment automation scale faster than governance. So, these are the key challenges you’ll face when applying continuous deployment at scale:
- Risk of unstable code reaching production: Without a manual approval step, even small logic errors can move straight into live environments. Forrester’s Global DevOps Benchmark Survey found that only 45% of organizations automate release to production. This shows how many teams still hesitate to hand this responsibility fully to automation. In the context of continuous deployment, this hesitation makes sense: full release automation requires a high level of trust in your validation, rollback, and monitoring systems. Strong pre-deployment validation and structured build configuration management reduce the risk.
- High dependency on test automation and monitoring: Gaps in test coverage or alerting usually stay invisible until a failure hits production. Automated validation must cover performance and security checks to confirm that every release meets reliability and stability standards.
- Cultural resistance and trust gaps: Moving from manual control to automation changes accountability. In the study “Automation from the Worker’s Perspective,” many workers acknowledged automation’s benefits but voiced concern about its risks, especially around oversight and reliability. This hesitation usually appears when automation replaces individual control. This leaves your team confused about ownership and accountability during a failure.
Continuous Deployment Metrics
The right metrics give you the clearest view of how well your delivery system performs. They help you see where speed translates into value and where reliability might be slipping. These are the key variables that indicate how healthy and mature your deployment process truly is:
- Deployment frequency: It shows how often your team deploys to production each week. According to the 2024 DORA Report, high-performing teams deploy multiple times per day. Smaller code batches make each release easier to predict and control.
- Failed deployment recovery time, formerly Mean time to recovery (MTTR): This tracks how fast you can restore service after a failed deployment. The same DORA report notes that elite teams typically resolve incidents in under one hour, which limits customer disruption and operational loss.
- Deployment failure rate: This measures the percentage of deployments causing service degradation. In top DevOps organizations, the rate stays near 5%, which reflects mature validation and rollback practices.
- Deployment time: Measured as the gap between a pull request merge and production release. At Axify, we believe that high-performing teams complete this in under two hours when automation is fully enabled.
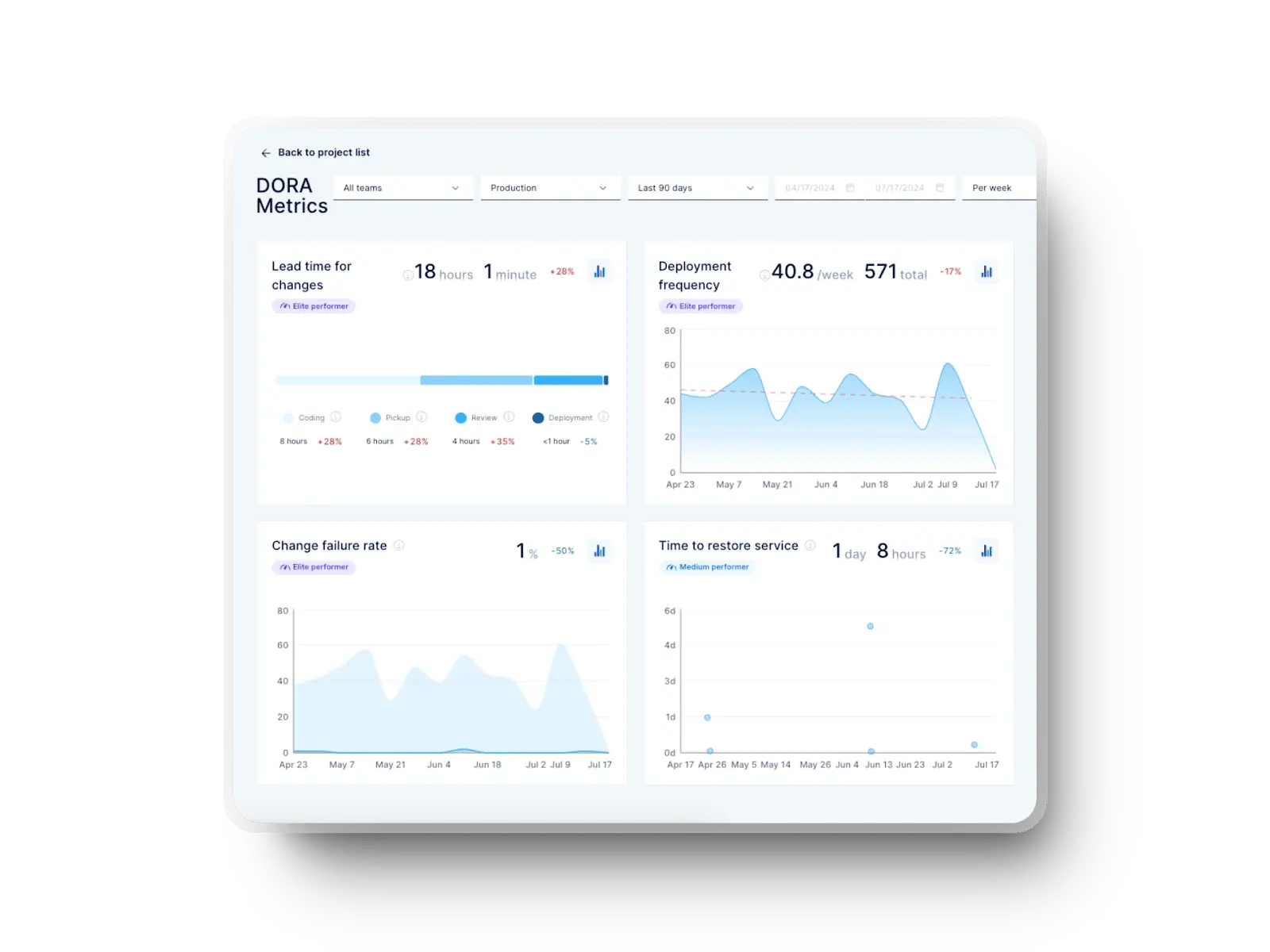
- Rollback rate: This shows how frequently code must be reverted after release. A rising rollback rate signals unstable testing or missing quality gates in your build history or staging validation.
- Production downtime: It measures how long systems are unavailable during deployment. Even brief outages can hurt customer satisfaction, especially in continuous services like eCommerce or SaaS.
- Uptime: The inverse of downtime, uptime tracks how frequently systems remain accessible during deployments. Maintaining consistent uptime demonstrates both technical stability and strong operational planning.
Together, these metrics provide a balanced picture of delivery performance and resilience. Next, let’s discuss the most effective tools that help you measure and automate these metrics in practice.
Continuous Deployment Tools
The right tools make automation reliable, scalable, and secure. They orchestrate the entire flow from code validation to production deployment, so every build that passes tests can be deployed safely and consistently. This gives your engineering team full visibility into every step of the deployment process and makes it easier to manage large-scale, continuous deployment pipelines effectively.
Here are the tools to get started:
1. Argo CD
A declarative, GitOps-based deployment tool built for cloud-native environments. It synchronizes your application state directly from your Git repository. That way, production always mirrors the source of truth.
Argo CD supports multi-cluster delivery and enables real-time rollbacks. This makes it ideal for organizations running workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine or similar platforms.
2. Spinnaker

Known for handling complex pipelines across multiple clouds, Spinnaker excels in large enterprises with hybrid or on-prem infrastructure. It supports advanced deployment strategies like canary and progressive delivery.
This gives teams full control over how new versions reach users. Integration with monitoring tools adds a safety layer for post-deployment verification.
3. GitLab CI/CD
This all-in-one solution ties version control systems, testing, and deployment into one pipeline. It provides role-based access management to control permissions while maintaining audit trails across teams. Its built-in container registry and artifact registry integrations make artifact handling simple and traceable.
4. GitHub Actions
A flexible automation framework within GitHub that connects code commits to deployments through event-driven build triggers. It’s favored by development teams seeking tighter integration between coding, testing, and production, without relying on external orchestration.
5. CircleCI
A scalable platform that supports rapid iteration with strong insights into build history and pipeline efficiency. Its configuration flexibility and analytics dashboard make it especially effective for teams that iterate frequently across multiple microservices.
Continuous Deployment Platforms
Choosing the right platform determines how effectively your pipelines scale and how seamlessly your code is deployed to production after validation. The tools below act as orchestration layers (coordinating builds, releases, and monitoring across complex environments with high automation needs).
1. AWS CodePipeline

Built for teams that already operate within the AWS ecosystem, CodePipeline automates every stage of build, test, and release. It integrates directly with services like CodeBuild, Lambda, and CloudFormation.
This allows you to manage deployments without leaving the AWS console. The benefit is consistency. Every release follows the same process and reduces the chance of configuration drift or manual errors.
2. Azure DevOps
A strong option for organizations balancing both cloud and on-prem systems. Its pipelines support multi-stage releases, approval gates, and environment tracking in a single dashboard.
It integrates deeply with Azure Functions and Kubernetes to streamline delivery. This alignment helps you connect development and IT operations without adding extra tooling overhead.
3. Google Cloud Build
This fully managed service focuses on speed and scalability. It runs builds in isolated containers, which keeps pipelines secure while maintaining high throughput.
When combined with services like Cloud Deploy and Artifact Registry, Cloud Build simplifies end-to-end delivery. It’s especially effective for containerized workloads running on Google Kubernetes Engine.
4. GitLab

GitLab acts as both a platform and a control center. It combines source code management, CI/CD, and security into one streamlined workflow.
Its flexibility allows you to build, test, and deploy from a single repository. This makes it easier to track every commit through to production.
5. Harness
Harness is known for its intelligent automation. The tool uses machine learning to detect anomalies during deployment and automatically roll back unstable releases.
It also includes built-in cost tracking. This gives teams visibility into how frequent deployments impact infrastructure spending.
Continuous Deployment Best Practices
Adopting automation alone doesn’t make your deployment and release process reliable. True consistency comes from disciplined workflows that protect quality while sustaining speed. These are the practices that keep your delivery pipeline predictable and secure under real production pressure.
Implement Strong Test Automation
Automated testing must go beyond unit checks. It should validate integrations, APIs, and user-facing behavior before code reaches the production environment.
Teams that invest in comprehensive test suites spot defects earlier, which helps them save time later in the cycle. The goal is coverage, but the right ones are tied to high-risk components.
Shift-Left Testing
The sooner you test, the cheaper the fixes become. Shift-left validation earlier in the development cycle lets engineers detect logic flaws during commit or build stages, rather than after deployment. It shortens feedback loops and gives your team confidence that production is receiving clean, stable code.
Use Canary or Blue-Green Deployments
Rolling out updates gradually limits exposure when bugs slip through. Canary deployments are released to a small percentage of users first. This allows you to monitor live performance and roll back quickly if needed.
Blue-green setups keep two identical environments. One live, one idle, so that you can switch traffic instantly with zero downtime.
Monitor Production in Real Time
Once your updates go live, visibility becomes your safety net. Real-time monitoring tools detect anomalies in system performance, error rates, or user behavior before they escalate. Correlating metrics from infrastructure and application layers helps you pinpoint root causes fast, which cuts recovery time significantly.
Have Clear Rollback Strategies
Automation should never remove human judgment. A well-defined rollback plan outlines when and how to revert code safely. Version control practices and backup snapshots make rollbacks fast. This reduces the impact on users and maintains trust in your delivery system.
Feature Flagging for Safety
Feature flags give you control after release. They let you toggle functionality on or off without redeploying, which keeps risk low during large-scale updates. This also enables controlled experiments. You can expose a feature to specific user groups and measure outcomes before full rollout.
FAQ
Axify connects engineering metrics with deployment outcomes. It tracks delivery speed, stability, and team flow. This gives you real insight into how to deploy more frequently with less risk.
If you’re ready to accelerate with confidence, contact Axify to see how your team can scale smarter.






.png?width=60&name=About%20Us%20-%20Axify%20(2).png)


