You’ve probably asked yourself why your development teams are stuck in endless cycles with delays, rework, and missed deadlines. Well, this doesn't mean that your team should work harder. But you do need to understand where the real inefficiencies lie in your software development lifecycle.
For that reason, in this article we’ll explain how to pinpoint those friction points, measure true efficiency, and take action to break through the barriers slowing down progress.
Side note: It’s how we helped clients like Newforma deliver 22x more often with a 95% shorter delivery time.
So, let's get to it.
What Is Software Development Efficiency?
Software development efficiency is the ability to deliver high-quality software with minimal friction and wasted effort. Of course, we don’t encourage you to focus purely on speed. You’ll want to balance throughput and quality with speed in a way that consistently meets business objectives.
When your process is efficient, your teams move from one stage to the next without bottlenecks, which reduces waiting time and rework. This efficiency is closely tied to the flow-based thinking outlined in the Flow framework. Adopting this mindset ensures that work progresses smoothly through each phase of the development lifecycle.
Here's how you can maximize efficiency in software development:
Productivity vs. Engineering Efficiency
Productivity is the total amount of work done in a given time, while engineering efficiency focuses on improving the process itself.
Productivity is measured by developer productivity metrics. However, we admit that it’s sometimes easy to get lost in these numbers and miss the bigger picture.
Engineering efficiency ensures that teams aren’t just producing more work but delivering better results with fewer resources. So, speed alone, like in the case of development velocity, isn’t a good indicator of success.
Focusing too much on that speed (and individual productivity/ efficiency poorly understood as busyness) can lead to mistakes, technical debt, and decreased quality. This ultimately undermines the efficiency of the whole team.
Operational Software Development Efficiency
Efficiency in software development is also reflected in the speed of build, test, and deploy cycles. CI/CD practices that automate testing and deployment help to reduce these cycle times, which enables quicker, more reliable releases.
The faster you can build and deploy with confidence, the less time is spent on waiting and fixing issues that could have been avoided with smoother processes.
For example, we helped two teams at the Development Bank of Canada 10X ROI and 2X delivery time.
We allowed them to find and reduce inefficiencies, which led to faster value creation and better team predictability. Our audit revealed three opportunities for acceleration: pre-development, QA, and task planning.
Results speak for themselves:

All of this takes us to our next point.
How to Measure Efficiency in Software Development: Software Development Efficiency Metrics
At Axify, we believe that measuring software development efficiency requires tracking key metrics that reveal bottlenecks and friction points in your workflow. These metrics allow you to pinpoint where delays occur and understand their operational impact.
Axify helps visualize these metrics to give you a clear picture of efficiency in action.
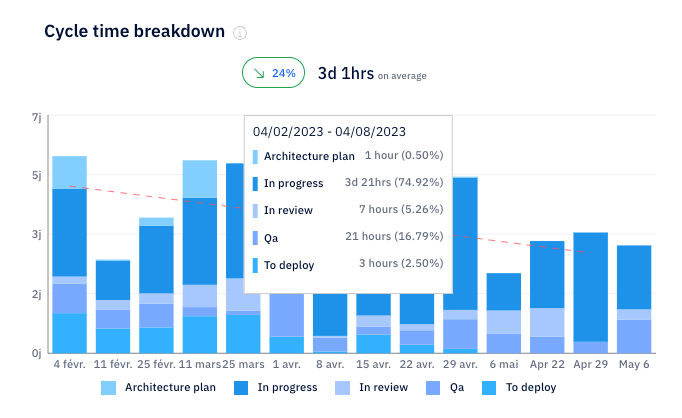
Cycle Time
Cycle time measures how long it takes for a piece of work to move from start to finish. It includes everything from the moment a task enters the backlog until it's deployed.
Axify shows you cycle time trends and helps you spot stages where delays accumulate. Here's what that looks like from one of our demo projects:
Lead Time for Changes
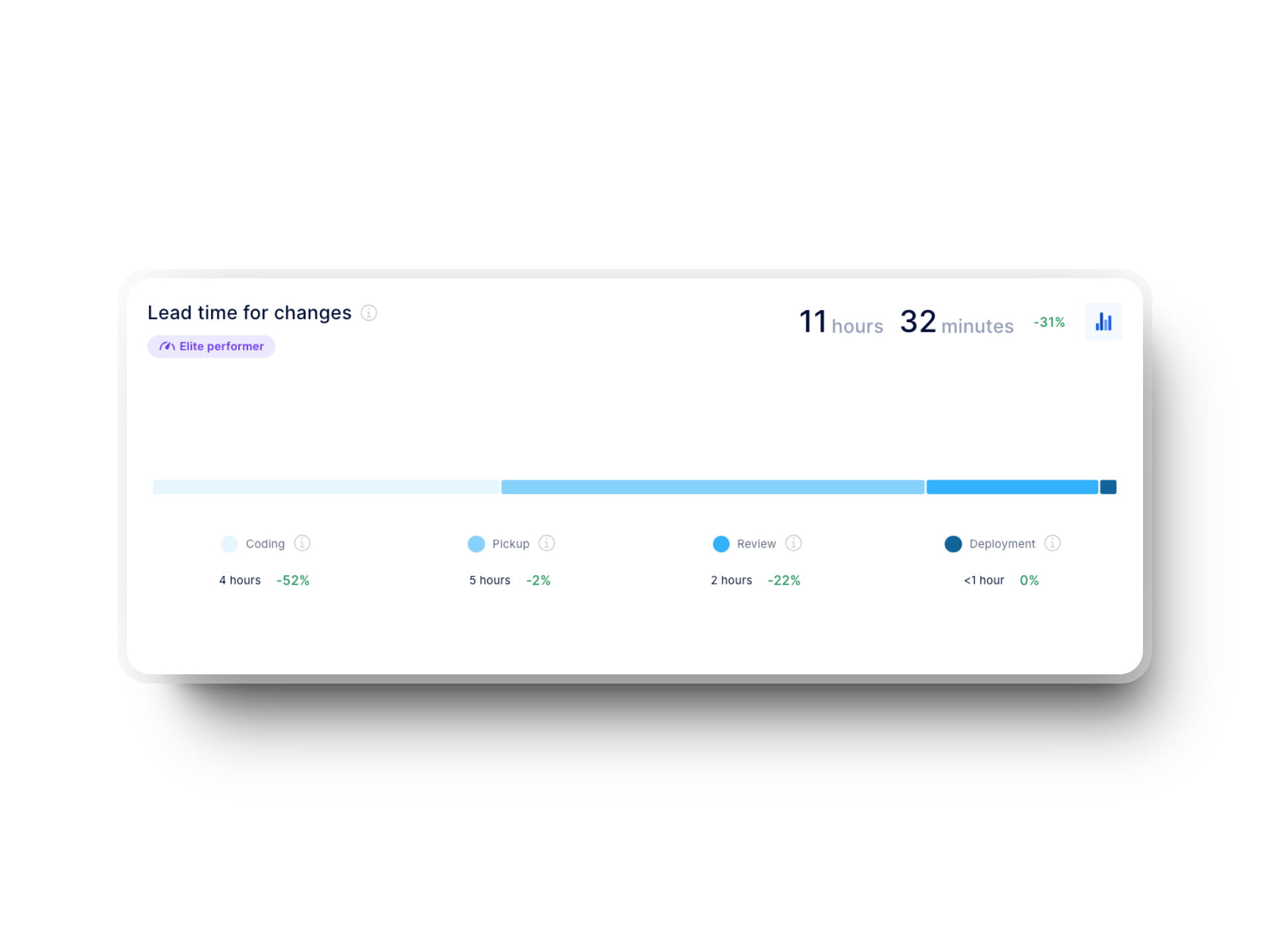
Lead time for changes measures how long it takes for a code change to move from commit to running in the production environment. It reflects how quickly you respond to user needs and, therefore, your business demands.
But how fast can high-performing teams genuinely deliver value?
Well, according to the DORA 2025 report, 9.4% of teams achieve lead time for changes in less than one hour.
Axify makes it easier to monitor your results so you can ultimately improve them. It can show how long each step in the development lifecycle takes. Here's what that looks like in action:
Deployment Frequency
Deployment frequency tells you how frequently you’re able to deploy code to production. More frequent deployments indicate smoother and more efficient pipelines. However, the DORA 2025 report reveals that 16.2% of teams deploy on demand, which should be the ideal.
Axify gives you good insights into your team’s delivery cadence. You’ll see deployment frequency trends over time, average deployments per day, total deployments, and whether delivery speed is improving or slowing down. You’ll even see your performance status, as shown below:

Mean Time to Recovery (Failed Deployment Recovery Time)
MTTR, now called Failed Deployment Recovery Time, measures how quickly teams can recover from failed deployments. Shorter MTTR means less disruption and faster recovery. For a clear benchmark for your team, the DORA 2025 report shows that 21.3% of teams recover in less than one hour.
Axify helps track this value, so you can improve response times. You can measure it easily in our dashboard, looking at incident duration, resolution date, and the overall trend:

Change Failure Rate
Change failure rate tells you the percentage of changes that fail after deployment. Lower rates suggest more stable releases. But according to the DORA 2025 report, only 8.5% of teams have a change failure rate between 0% and 2%.
Axify tracks this metric by integrating data from your deployment pipelines. You can check it out here:

In this view, you can see how your change failure rate evolves, along with the current percentage, a performance benchmark (for example, Medium performer), and daily deployment activity. Hovering over any data point shows how many deployments failed on a given day and how that contributed to the overall rate.
Code Churn / Rework
Code churn refers to the amount of code that is rewritten after being submitted. High code churn indicates inefficiencies in the review or testing process. The DORA 2025 report shows that 6.9% of teams have a rework rate between 0% and 2%.
This range is generally associated with high-performing teams, where changes are well-scoped, reviewed early, and tested before merge.
However, very low churn isn’t always the goal.
Some level of rework is normal, especially in fast-moving teams that iterate quickly or explore new solutions. What matters most is keeping churn predictable and intentional, rather than reacting to avoidable fixes caused by unclear requirements, late feedback, or gaps in testing.
Flow Efficiency
Flow efficiency shows how much time work is actually being worked on versus how much time it spends waiting. In other words it measures how much time your team spends on tasks that add value versus time spent waiting for feedback, approvals, or resources. Surveys indicate that many teams have flow efficiency in the single digits, up to around 15%.
Axify provides a clear breakdown of your flow efficiency, complete with the cost of that time. This can help you target delays and interruptions, and see how much you ultimately save after solving those issues.

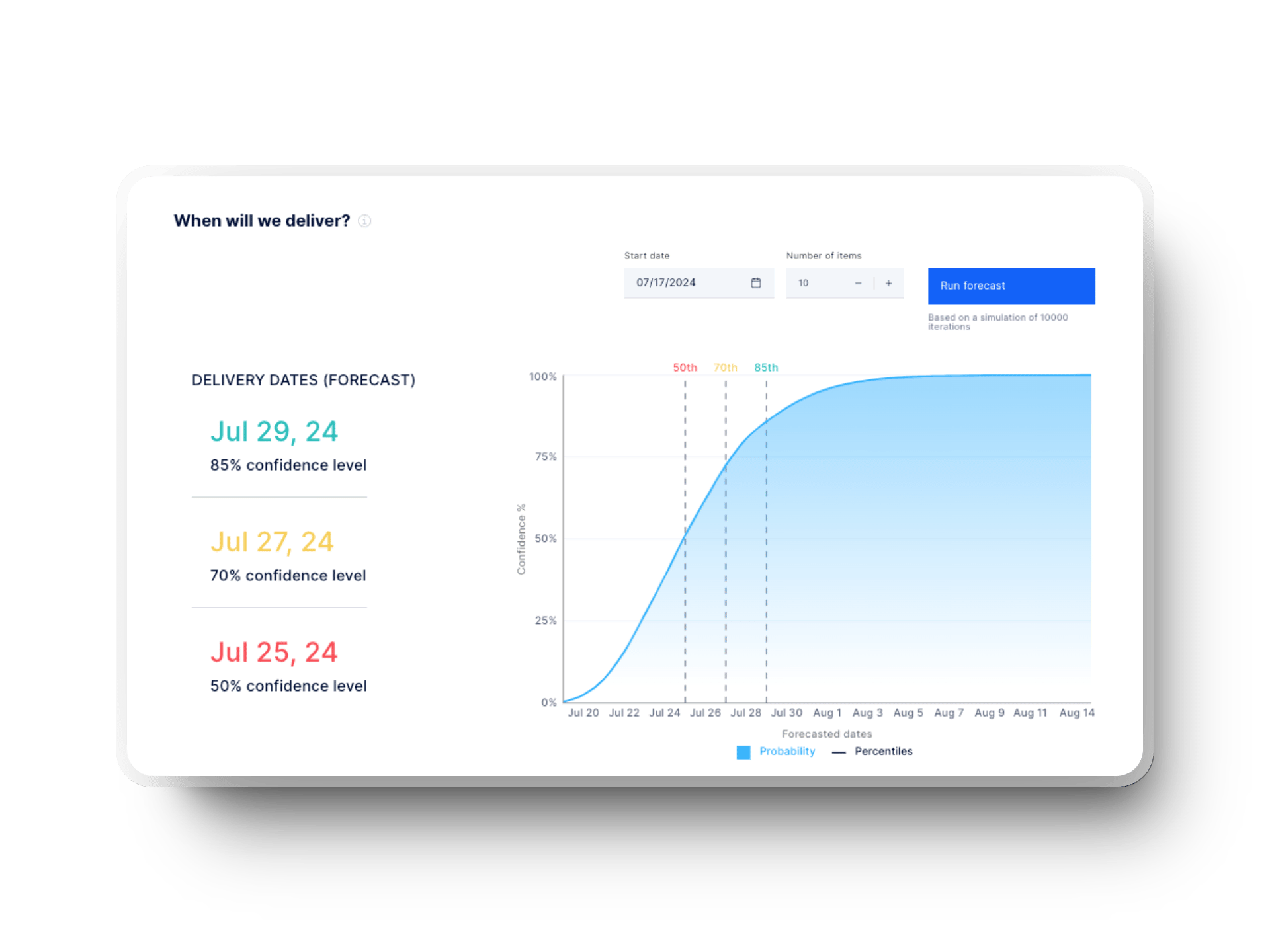
Time to Delivery
Time to delivery measures the overall time it takes to deliver a feature from ideation to production. It’s one of the most critical efficiency metrics. In large IT project studies, only 29% of software or IT projects finish on time and on budget.
Axify estimates time to delivery within this software delivery tracker. You can track different forecast dates, each with a different probability level, so you can plan accordingly. If you’re unhappy with these estimates, you can look into potential blockers to streamline your delivery timeline.
Time to Delivery Before/ After AI Implementation
When AI-driven tools are introduced into teams with streamlined processes, time to delivery can be drastically reduced. By automating parts of coding, testing, reviews, and deployment, teams can focus on higher-value work and deliver faster.
Pro tip: The results are nuanced, which is why we analyzed the impact of AI on software development in a separate piece. Read it to understand its benefits and risks, and how to implement it correctly from the start.
Axify visualizes the impact of generative AI on your team’s efficiency before and after AI with this AI Performance Comparison tool.
Below, you can see how this time to delivery varies according to the AI adoption rate:
.png?width=2441&height=1484&name=AI%20Impact%20Beautyshot%20-%20FR%20(1).png)
Now, let's see what poor visibility can cost you.
The Costs of Poor Efficiency in Software Development
When software development efficiency is lacking, the consequences go beyond just slow delivery. Operational bottlenecks and inefficient processes compound over time, which leads to high costs for both your team and the business.
So, let’s break down how poor efficiency affects your teams and bottom line.
What Causes Poor Software Efficiency?
The root cause of poor software efficiency is usually tied to friction in your processes and systems. Here are the key contributors:
- Poor requirements: Unclear or changing requirements lead to wasted effort and rework.
- Inefficient processes: Lack of standardized workflows results in delays and communication breakdowns.
- Lack of CI/CD automation: Without automation, teams lose time on manual tasks, which reduces speed and increases error rates. In fact, teams without CI/CD automation can lose around 20% of their development time to manual testing.
- Poor architecture / technical debt: Legacy systems and poorly designed architecture slow down progress and increase complexity.
- Lack of flow visibility makes it hard to see where work is waiting. This leaves bottlenecks hidden behind healthy-looking engineering metrics.
- Collaboration gaps: Silos between teams lead to delays in feedback and decision-making, hindering overall flow.
The Impact of Poor Software Development Efficiency
Inefficiency has far-reaching consequences for the business. In our experience, these include:
- Business costs: Missed market opportunities and delayed product releases mean falling behind competitors and losing customers.
- Developer frustration + attrition: When engineers are constantly fighting bottlenecks and rework, frustration builds, which leads to burnout and turnover.
- Higher defect rate: Slow feedback loops and poor architecture typically result in a higher defect rate. This leads to more downstream rework and delays.
The financial impact of continuous improvement is clear: addressing inefficiencies upfront saves time and resources in the long run.
That’s why we like to map out the improvements we can execute for our clients, and tie them to specific outcomes. Here’s what that looked like for our client Newforma:

Side note: You can read more about the ROI of optimizing your workflows in our guide on continuous improvement.
These hidden costs erode the potential for growth and innovation within your engineering teams and the broader organization. So, addressing inefficiencies now can help you break the cycle and pave the way for smoother, faster deliveries.
7 Steps to Increase Software Development Efficiency
Improving efficiency means changing how work flows through your system rather than pushing teams to move faster. The steps below focus on removing friction where it actually forms and making delivery behavior visible and manageable.
Implement CI/CD Pipelines
CI/CD pipelines reduce waiting time between code changes and production readiness. Without them, work piles up in testing and release phases.
The problem is that only about 35% of organizations have fully adopted CI/CD pipelines, which leaves the majority dependent on manual handoffs. As part of broader DevOps practices, CI/CD creates predictable delivery paths and lowers risk during change.
Adopt Flow Visualization
Flow problems stay hidden until you make them visible. Flow visualization methods, such as Axify's value stream mapping or delivery views, show where work waits rather than just where it moves.
When flow is visible, task delays stop being anecdotal and become measurable. That visibility gives you a clear place to intervene instead of guessing.
Here's how value stream mapping looks within Axify:

Improve Cross-Team Collaboration
Delivery slows when ownership breaks across teams. And handoffs between product, platform, and application groups introduce queues and misaligned priorities.
So, improving collaboration means tightening feedback loops across organizational structures. Clear ownership and shared delivery goals reduce coordination overhead and stalled work.
Remove Bottlenecks Through Regular Flow Reviews
Bottlenecks shift over time. Regular flow-focused retrospectives help teams identify where work is slowing down now, not where it slowed down last quarter.
By reviewing real delivery data, teams uncover systemic constraints rather than relying on intuition or outdated assumptions.
Invest in Automated Testing
Testing late in the pipeline increases rework and release risk. And from our experience, automation shortens feedback cycles and stabilizes delivery.
This shift is already underway. According to the 2025 State of Continuous Testing, over 75% of respondents identified AI-driven testing as a key part of their strategy. The rise of AI developer tools reflects a move toward earlier and more consistent validation.
Build Observability Into Delivery
Operational visibility should extend beyond runtime metrics.Delivery observability connects code changes, pipeline stages, and outcomes into a single view. This connection makes it clear how decisions impact lead time, failure rates, and recovery patterns across the system.
Address Tech Debt Through Architectural Simplicity
Complex systems slow change. Simplifying dependencies and clarifying ownership reduces the cost of every update. A modular architecture enables independent change, while unchecked microservices sprawl often does the opposite.
Next, let’s look at how AI changes delivery behavior and where it fits into the system.
Improving Efficiency in Software Development: AI Tools You Need
AI changes efficiency only when it removes friction from real delivery paths. When used well, it shortens feedback loops and reduces manual effort. But when used poorly, it adds noise. The difference comes down to where AI fits into your system.
AI-assisted coding tools like Copilot and Cursor can speed up routine work inside the editor. They’re particularly effective for scaffolding, refactors, and common patterns. Their impact is most visible when suggestions reduce context switching and keep developers focused inside existing workflows.
Pro tip: We’ve discussed whether AI coding assistants really save developers’ time, analyzing the current data to uncover when they can work and when they create new bottlenecks.
AI-driven test generation targets a different constraint. Late feedback typically slows delivery more than coding itself. But automated test creation moves validation earlier, which reduces rework and stabilizes releases. That shift matters because failures caught late ripple through schedules and undermine your team’s confidence.
Code quality checks powered by generative artificial intelligence (genAI) can surface risk before changes merge. These checks work best when tied to pull request workflows, where feedback still changes outcomes instead of documenting problems after the fact.
Delivery insights sit at the system level. Axify uses AI to connect pipeline data, flow metrics, and outcomes across teams. Instead of isolated productivity metrics, you see patterns in waiting time, failure recovery, and throughput across your software development cycle.
Moving on, we'll clarify who owns efficiency across the organization.
Who Makes Software Development Efficient in a Company?
Software development efficiency is shaped by shared ownership across roles and not by a single team or function. Each group influences how work flows, where it slows down, and how risk accumulates over time.
Here's how that looks:
- Engineering leaders carry responsibility for team-level efficiency by setting delivery constraints. They limit work in progress and decide which tradeoffs are acceptable under pressure. They also monitor their teams’ performance and make adjustments when needed.
- Product managers affect efficiency through requirements clarity and sequencing. Poor prioritization creates rework and delays long before code is written.
- Architects shape how easily change moves through the system. Decisions around modern architecture either reduce friction or lock teams into slow deliveries.
- DevOps and platform teams influence how reliably work moves from commit to production. Their choices determine whether pipelines support flow or introduce waiting.
- Individual engineers affect efficiency through daily decisions that compound over time, from review discipline to coordination habits shaped by human factors, such as interruptions, context switching, and unclear ownership.
What matters most is how these roles interact. A Deloitte study found that 73% of employees working collaboratively report better performance. In other words, efficiency improves when responsibility is shared, and incentives stay aligned across teams rather than optimized in isolation.
But how can you implement all of this?
Software Development Efficiency Program: Best Practices to Implement at an Organizational Level
A sustainable efficiency program takes shape at the organizational level, where incentives, visibility, and decision responsibilities intersect. The focus here stays on system behavior rather than isolated team actions.
The following practices show what engineering leaders and team leads typically do to make efficiency durable.
Continuous Improvement Mindset
Our team believes that efficiency improves when inspection becomes routine. Regular review of delivery outcomes keeps attention on where work slows and why. This discipline prevents small delays from turning into structural drag.
Agile and Lean Principles Focused on Value
Applying Agile and Lean principles (or even Lean-Agile methodologies) works when you prioritize value flow over ceremony. The tradeoff is clear. Excess structure slows response, while too little structure hides risk. A value-first lens keeps work aligned with outcomes rather than activity.
Leadership Buy-In with Flow KPIs
Leadership support matters when it anchors decisions in flow KPIs. Metrics tied to throughput, recovery, and waiting time guide tradeoffs across teams. This approach aligns priorities and reduces debates driven by opinion instead of evidence.
Cross-Functional Ownership
Efficiency breaks when ownership fragments. So, shared accountability across product, engineering, and operations reduces handoff delays.
This is already the norm in many environments. PMI data shows that half of project professionals work in cross-functional setups, which explains why coordination quality directly affects delivery speed.
Learning and Feedback Loops
Fast feedback limits rework. Learning loops tied to delivery data help teams adjust before problems compound. This practice supports better resource efficiency by reallocating effort away from stalled work.
Avoid Local Optimization Through System Thinking
Local gains usually shift pressure elsewhere. A team that optimizes throughput can overload downstream stages. But systems-level thinking focuses on balancing capacity across the full delivery path so work continues to flow without new constraints forming.
Continuous Monitoring of Efficiency Metrics
Metrics lose value when reviewed quarterly. Continuous tracking connects decisions to outcomes in near real time. This visibility also reveals how inefficiencies drive up infrastructure costs through idle capacity and longer recovery windows.
With the program-level foundation in place, the next step focuses on hands-on practices teams apply day to day.
Hands-On Practices for Developers to Improve Efficiency
Efficiency improves when daily engineering habits reduce waiting, rework, and coordination overhead. At the team level, these practices focus on how code moves, how feedback arrives, and how decisions compound over time.
Here are practical actions developers and teams use to keep work flowing:
- Trunk-based development (TDD): Short-lived branches reduce merge risk and integration delays. Frequent integration keeps feedback close to the change and prevents late surprises that stall releases.
- Small pull requests: Smaller changes move through review faster and lower cognitive load. Review quality improves because intent stays clear, and rework drops because feedback arrives before context fades.
- Limit work in progress: Too many active items stretch attention and slow completion. Limiting WIP reduces task switching and exposes real constraints instead of masking them with parallel effort.
- Shift-left testing: Earlier validation shortens feedback loops and cuts downstream fixes. Catching issues close to implementation reduces the ripple effect that usually delays testing and release stages.
- Continuous integration and continuous delivery: Frequent integration keeps the system releasable. Automated pipelines extend integration into delivery, so changes move forward as soon as validation passes.
- Use abstractions to simplify development: Clear boundaries reduce how much of the system each change touches. APIs, platform services, and shared components isolate complexity so teams can work without coordinating every detail. Well-chosen abstractions protect flow by hiding internal mechanics that do not affect outcomes.
- Automated testing: Automation stabilizes delivery by making validation repeatable. When tests run consistently, confidence increases, and manual checkpoints stop delaying progress.
- Clean code practices: Readable structure and clear intent reduce future rework. Changes become easier to reason about, which shortens review cycles and lowers the risk of unintended side effects.
- Pair programming and code reviews: Early collaboration reduces misalignment and spreads context. Shared understanding lowers dependency on individual experts and prevents bottlenecks from forming around specific reviewers.
When taken together, these practices reduce invisible delays and protect delivery flow. Each one limits how friction accumulates, which allows teams to complete work instead of carrying it forward unfinished.
Streamline Your Software Development Efficiency with Axify
Software development efficiency determines how reliably work moves from idea to production without accumulating delay, risk, or rework. When flow breaks, effort increases while outcomes slip.
Tracking delivery health makes those breaks visible before they turn costly. With Axify, that visibility comes from real delivery data.
Book a demo to see where flow slows and where change will matter most.
FAQs
How does CI/CD improve software development efficiency?
CI/CD improves software development efficiency by reducing waiting time between code changes and production readiness. Automated pipelines keep the system releasable and surface issues as soon as validation completes.
How do APIs improve the efficiency of software development?
APIs improve the efficiency of software development by isolating change and reducing cross-team coordination. Clear contracts allow teams to work in parallel without renegotiating internal behavior.
How does Infrastructure as Code (IaC) improve software development efficiency?
Infrastructure as code improves software development efficiency by making environment changes predictable and repeatable. That consistency removes manual setup delays and reduces release risk.
How can Axify help me improve software development efficiency?
Axify helps you improve software development efficiency by making flow, delays, and outcomes visible across your delivery system. That visibility supports targeted changes and allows you to track how it evolves over time.






.png?width=60&name=About%20Us%20-%20Axify%20(2).png)


