Updated for 2025: This guide now includes AI-related engineering metrics and the latest DORA benchmarks.
You're on the right page if you're looking for the best DORA metrics tools.
After we share our five-step framework, which includes metrics measurement, developer friendliness, integrations, and more, we'll analyze six top contenders.
Feel free to use it if you're doing your own shortlist.
Here's a sneak peek:
|
Tool |
Metrics measurement |
Developer friendliness |
Integrations |
Data reliability and performance |
Support and resources |
Average score |
|
Axify |
5 |
5 |
4.5 |
5 |
4.75 |
4.85 |
|
LinearB |
5 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
4.5 |
4.3 |
|
Swarmia |
5 |
4.5 |
4 |
4.5 |
4 |
4.4 |
|
Jellyfish |
5 |
4 |
3.5 |
4.7 |
3 |
4 |
|
Allstacks |
5 |
4 |
4.5 |
4.7 |
4 |
4.4 |
|
Sleuth |
5 |
4 |
4.5 |
4.5 |
4 |
4.4 |
Insider tip: Use Axify if you want a tool that combines DORA software metrics with unique features like Developer Productivity Measurement, VSM, and AI Performance Comparison. We offer actionable insights beyond standard metrics, improving your performance and team dynamics.
What Are DORA Metrics?
DevOps Research and Assessment (DORA) metrics are performance indicators for multidisciplinary teams (i.e., development and operations teams). You can use them to gain valuable insights into your software development lifecycle.
Following DORA metrics allows engineering teams, software leaders, and other stakeholders to make data-driven decisions based on team performance. The end goal, of course, is to improve operational efficiency and, as a result, customer retention and satisfaction.
Insider tip: At Axify, we advise our customers to consider operational efficiency in the context of team dynamics. Use the metrics below not to place blame but to find actionable insights that help the entire team.
![]()
Download our free DORA metrics E-book 👇
1. Deployment Frequency
Deployment frequency measures the number of times a team successfully releases to production over a given period. Frequent deployments indicate a smooth and efficient deployment process, which can lead to faster feedback and improvement cycles.
Pro tip: One key advantage is that our tool detects deployments from multiple sources. This way, you get comprehensive tracking even if teams ship through different tools or workflows.

2. Lead Time for Changes
Lead time for changes measures the period it takes for a committed code change to reach production. Shorter lead times indicate a more efficient development process because teams respond quickly to changes and feedback. That improves user and developer experience.

3. Change Failure Rate
Change failure rate measures the percentage of deployments causing failures in production requiring remediation (e.g., hotfix, rollback, patch). This metric shows whether you have good code quality and a reliable deployment process. Also, a lower change failure rate suggests better code and processes, which lead to higher customer satisfaction.
Pro tip: Axify can help you there because it associates an incident with its last deployment.

4. Failed Deployment Recovery Time
This metric measures the time it takes for a team to recover from a production failure and restore service to users. It helps you understand the effectiveness of incident management and response workflows. Faster recovery times are better because they enhance operational performance and minimize customer impact.
%20in%20axify%20for%20software%20development%20teams.webp?width=851&height=638&name=time%20to%20restore%20service%20(dora%20metrics)%20in%20axify%20for%20software%20development%20teams.webp)
How to Choose a Good DORA Metrics Tool
As you can see, all the metrics above have their own measurement challenges. Getting an accurate read on your current situation can be difficult because of factors like inconsistent data, variability in how metrics are defined across teams, or gaps in your toolchain integration. These challenges can lead to incomplete insights and skewed results, making it harder to drive meaningful improvements.
You must select the right tool to build a comprehensive DORA metrics dashboard and avoid these mistakes.
From our experience at Axify, we encourage you to consider the following criteria to make an informed choice.
Pro tip: We’ll show you how we use these criteria in the next section, where we analyze 13 top DORA software metrics tools.
1. Metrics Measurement
A good tool should cover all essential metrics and provide actionable insights to accurately measure your team's DevOps performance. Here are some questions to help assess a tool's metrics measurement capabilities:
- Does the tool cover all four DORA metrics? Ensure the tool provides comprehensive coverage of the four indicators we discussed above.
- How are the metrics visualized and reported? Look for intuitive dashboards that make it easy to interpret data and make informed decisions.
- Does the tool provide organization-wide insights? Some tools, like Axify, allow you to view DORA software metrics across the entire organization. This lets you see performance metrics for all projects or teams simultaneously, making monitoring and comparing performance across your organization easier.
- Can we trust the data's accuracy? Check if the tool allows you to quickly drill down into the data, view historical data, and validate its accuracy. A tool that can do this is more reliable because it helps you make data-driven decisions based on accurate insights.
2. Developer Friendliness
A developer-friendly tool ensures your team adopts and uses it effectively. Consider the following questions:
- Is the tool easy to use and understand? The interface should be intuitive, allowing developers to quickly access the information they need without a steep learning curve.
- Does it provide valuable insights without overwhelming users? Look for a balance between detail and simplicity. You need actionable insights that aren't overly complex.
- How does the tool support continuous improvement? Ensure the DORA metrics tool facilitates a culture of continuous integration and improvement by providing feedback loops and highlighting opportunities for improvement.
3. Integrations
The tool should offer flexible integrations to fit seamlessly into your existing workflows. Here are some questions to consider:
- Does it integrate with our existing tools and platforms? Check for compatibility with your code repository, project management tools, incident management systems, and other DevOps tools.
- How easy is it to set up and maintain integrations? Assess the tool's setup process and ongoing maintenance requirements to ensure it won't burden your engineering teams.
- How customizable is it to fit your workflow? Look for a tool that seamlessly integrates with your team's workflow without requiring your team to adapt.
- Does it support multiple sources? Ensure the tool can handle numerous repositories, deployments, and incident sources.
- Can you filter views by teams or repositories? Check if the tool allows you to filter and customize views, enabling you to focus on specific teams or repositories as needed.
- How does the tool handle incident tracking? Many tools naively track incidents solely through issue trackers like Jira, but a solid tool should support multiple impact sources. Look for solutions that go beyond bug tracking and support a variety of incident sources to provide a more complete picture of your production issues. As a side note, this is an area where tools like Axify outperform competitors like LinearB.
4. Data Reliability and Performance
Consider how reliable the tool is for syncing data and performance. Here are key questions to evaluate.
- How reliable is the data? Ensure the tool syncs regularly and consistently with minimal delays or issues.
- How long does it take to synchronize for the first time? Investigate how quickly the tool can sync your data from when it's connected. Fast and efficient syncing is crucial, especially for teams managing large codebases.
- Does the tool ensure data security? Some tools, like LinearB, clone repositories to calculate metrics, which raises security concerns. Look for solutions that extract only the necessary metadata, such as pull request metadata, to reduce security risks without compromising performance.
5. Support and Community
Reliable support and a tight user community can significantly impact your experience with the tool. Here's what to look for:
- What support options are available? Check for available support channels like chat, email, or phone, and whether there's a dedicated support team.
- Are there comprehensive resources available? Look for documentation, tutorials, and other learning resources to help your team get the most out of the tool.
Remember: Asking the right questions lets you choose a DORA metrics tool that supports your team’s goals, enhances your development process, and ultimately contributes to delivering high-quality software. At Axify, we advise our clients to prioritize tools that align with their specific needs and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
6. AI/Next-Gen Metrics
AI and automation add a new layer to how you understand engineering performance. These tools change how code is written, reviewed, and shipped, so you need metrics that capture this impact instead of relying only on traditional signals. They help you see how AI affects speed, quality, and everyday developer work.
Here are the key questions to guide your evaluation:
- Does it track AI adoption? Look for metrics like the percentage of developers using AI suggestions or automation so you can see how widely AI is embedded in daily work.
- Can it compare AI-assisted vs. non-AI work? The tool should help you contrast performance, quality, or speed between AI-generated and human-only work to understand the real impact.
- How does the tool measure AI-assisted work? Check if it tracks things like AI-suggestion acceptance, time saved through automation, or review cycles linked to AI-generated code.
- Does it separate AI-generated code from human-written code? You need this to understand code risk, churn, and stability.
- Can it point to quality issues tied to AI use? Look for insights on defect density, vulnerabilities, or rework triggered by AI-assisted changes.
- How does it support decision-making? A strong tool should show how AI impacts delivery outcomes so you can adjust processes, training, or team workflows.
These signals help you understand whether AI is actually improving your development process or creating hidden risks.
If you want a ready-made system for tracking DORA metrics, grab the checklist below. It gives you a clear, structured way to measure deployments, lead time, failure rates, and recovery times without missing key steps.
Download the DORA Metrics Implementation Checklist (PDF) 👇
DORA Software Tools List
Let's jump into the part you're here for.
1. Axify: Best for Tracking Metrics that Matter
Axify is a powerful platform designed to provide teams with a comprehensive view of their software development process. Axify helps engineering teams enhance their performance and deliver reliable software efficiently by tracking key metrics – from DORA to resource allocation and team morale.
Axify is an intuitive tool for different roles: engineering leaders and managers, product managers, and product operations professionals.
Insider tip: Leverage our unique team maturity assessment to get actionable recommendations to improve your software delivery performance. Elite performers with high DORA maturity are twice as likely to beat profitability, market share, and productivity targets. They also grew their market cap 50% faster in just three years.
Key Features
- DORA metrics dashboard: This dashboard provides real-time insights into all four DORA metrics, allowing teams to measure software delivery performance and make data-driven decisions. Pair this with Axify's Value Stream Mapping and objective tracking to track all essential metrics related to your business goals.
- Value Stream Mapping: Axify helps you visualize and optimize the flow of value from development to delivery, providing a clear picture of bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Organization-wide insights: Axify enables you to track DORA Metrics across all teams and projects, offering a comprehensive view of your organization's performance. This feature allows you to compare performance metrics across different teams and identify areas for improvement.
- Integration with DevOps tools: Axify seamlessly integrates with popular DevOps tools, such as code repositories and project management systems. This ensures smooth data flow and streamlined processes across all your metrics. However, other tools allow more integrations.
- Software delivery forecast: Axify calculates precise delivery estimates based on your historical data. Predictable software delivery is essential for maximizing your budget and offering top-notch solutions for your customers.
- AI Performance Comparison feature: This feature measures and compares your team’s performance with and without AI. As such, you can see AI’s impact on delivery time, DORA metrics, and other key indicators.
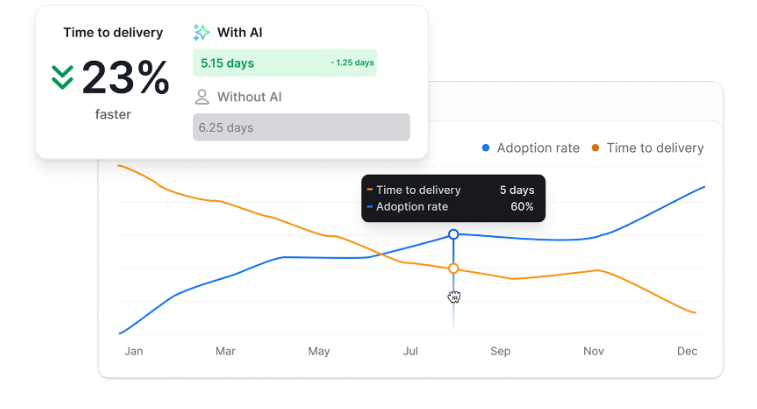
What Makes Axify Different
Axify shows a holistic view of DORA and a complete Value Stream Management (VSM) perspective, with visibility into flow metrics, bottlenecks, and overall delivery performance. It can also accommodate different teams, making it a versatile choice for organizations looking to optimize their software delivery process.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
5 |
|
Developer friendliness |
5 |
|
Integrations |
4.5 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
5 |
|
Support and resources |
4.75 |
|
Total |
4.85 |
2. LinearB: Workflow Automation and Developer Productivity Focus
LinearB centers on workflow automation and team-level metrics. The platform maps how work moves through the delivery pipeline and applies programmable rules to routine steps such as pull-request reviews, branch workflows, and handoff stages.
It reports DORA metrics within this broader workflow view. This gives teams a snapshot of cycle time patterns and delivery pacing without generating individual-level performance metrics.
LinearB also includes tools for resource allocation and project forecasting. These features estimate workload distribution and predict release timing based on historical activity.
Also, automation components like WorkerB and gitStream apply policy-as-code controls to standardize reviews and reduce delays in merge processes.
Pros:
- Automation around reviews and branch workflows.
- Team-level reporting instead of individual metrics.
- DORA metrics included in the general activity view.
Cons:
- Incident visibility is narrow because the platform depends mainly on issue trackers like Jira. This reduces visibility into incidents that originate from other sources, which some teams may need for broader production insight.
- LinearB clones full repositories to compute metrics. This increases the surface area for potential exposure, and some organizations may see this as a security concern.
- Insights are tied closely to how Jira and Git repositories are structured, which may reduce flexibility for teams with mixed systems.
Pricing: Starts at $19 per contributor per month.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
5 |
|
Developer friendliness |
4 |
|
Integrations |
4 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4 |
|
Support and resources |
4.5 |
|
Total |
4.3 |
3. Swarmia: Focus on Aligning Engineering Work with Business Objectives
Swarmia works as a work-management layer that connects engineering activity with business goals. The platform focuses on task prioritization, flow visibility, and team-level insights. It reports DORA and SPACE metrics and combines these with developer feedback to create a broad view of daily work patterns.
Axify offers similar capabilities with its Executive Dashboard.
This can help leadership measure the ROI of engineering efforts while maintaining a holistic view of the entire value stream.
But Axify goes a step further because it provides tools for the whole team so that everyone, from software engineers to product managers and CTOs, can access valuable, actionable insights.
Pros:
- DORA and SPACE reporting for trends and bottlenecks.
- Slack-based notifications that trigger feedback loops.
- Developer-experience signals tied to sentiment, cycle time, and work habits.
Cons:
- Metrics such as commit-to-merge time can be misused to compare teams or individuals, which creates pressure or incentives to game workflows.
- Limited integrations, with support focused mainly on Jira/Linear and GitHub.
- Narrower visibility into multi-source incidents compared to platforms that include more data inputs.
Pricing: Free for companies that have up to nine developers.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
5 |
|
Developer friendliness |
4.5 |
|
Integrations |
4 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4.5 |
|
Support and resources |
4 |
|
Total |
4.4 |
4. Jellyfish: Engineering Management and Alignment
Jellyfish gives engineering leadership a central view of how teams spend their time and how that work maps to organizational priorities. The platform aggregates activity data from tools like GitHub, Jira, and communication systems.
Then it structures that data into work categories, resource breakdowns, and delivery forecasts. Its focus remains on strategic oversight rather than day-to-day development work.
Jellyfish includes scenario-planning features that model different delivery timelines based on current staffing, historical performance, and project scope. It also focuses on resource allocation by showing how engineering hours are distributed across initiatives, teams, or product areas.
Pros:
- Consolidated resource-allocation views.
- Scenario planning for timelines and staffing.
- High-level reporting aligned with strategic initiatives.
Cons:
- Installation typically requires organization-wide administrative configuration.
- Some teams may need to adjust Jira workflows to fit Jellyfish’s data-mapping requirements.
- The platform is oriented toward executive and finance audiences, which limits value for individuals involved in hands-on software development.
- Limited flexibility if teams use multiple work-tracking systems outside the supported integrations.
Pricing: Custom quote.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
5 |
|
Developer friendliness |
4 |
|
Integrations |
3.5 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4.7 |
|
Support and resources |
3 |
|
Total |
4 |
5. Allstacks: Predictive Analytics in Software Delivery
Allstacks focuses on predictive forecasting and risk assessment in software delivery. It aggregates data from engineering and project-management tools and uses historical patterns to generate delivery estimates, identify risk areas, and map project health.
The platform's dashboards include a broad range of selectable metrics, which can create noise for teams that prefer a narrower, more streamlined view.
Meanwhile, Axify focuses on delivering only the most relevant metrics and removes dashboard clutter by connecting engineering performance directly to business outcomes.
Pros:
- Predictive analytics tied to software-delivery patterns.
- Risk-tracking views that map to project phases.
- Configurable dashboards for teams that want metric variety.
Cons:
- A large volume of available metrics can make it harder to maintain a clear signal-to-noise ratio.
- Customization options increase configuration work for teams that want a simpler setup.
- Forecasting models rely heavily on the accuracy of historical data, which may vary across teams or tools.
Pricing: $400 per contributor per year.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
5 |
|
Developer friendliness |
4 |
|
Integrations |
3.5 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4.7 |
|
Support and resources |
4 |
|
Total |
4.4 |
6. Sleuth: Deployment Tracking and Automation
Sleuth concentrates on deployment tracking and impact-based insights.
The platform centers its measurement model on deploy events rather than relying mainly on ticket updates or git activity. It then connects those deploys to issues, builds, and repository data to show what was shipped and how it affects the system.
Sleuth also reports the four DORA metrics and presents them in a delivery-focused view.
Sleuth includes several components that shape how teams observe deployments:
- Real-time views of deployment activity
- Impact markers tied to code changes
- No-code automation options through its automations marketplace
These automations standardize parts of the release process and reduce manual repetition.
Sleuth also includes review templates, AI-generated summaries for each metric, and fields for adding notes, review points, and action items directly within the dashboard.
Pros:
- Deploy-centric measurement model.
- Built-in automations for repetitive tasks.
- Metric summaries and review templates integrated into the dashboard.
Cons:
- The focus on deploy events may limit visibility into earlier workflow stages.
- No-code automations require configuration and tuning for teams with complex pipelines.
- Heavy emphasis on deployment data means teams relying on ticket-driven tracking may need to adjust existing workflows.
- Real-time tracking can introduce noise if teams deploy frequently without structured tagging.
Pricing: $35 per user per month.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
5 |
|
Developer friendliness |
4 |
|
Integrations |
4.5 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4.5 |
|
Support and resources |
4 |
|
Total |
4.4 |
7. Cortex: Driving Continuous Engineering Excellence
Cortex is an Internal Developer Portal that centralizes service data, engineering standards, and operational information. It brings multiple systems into one interface so teams can view ownership details, production requirements, and real-time service status without relying on separate tools.
The platform aims to streamline daily engineering workflows rather than operate as a traditional DORA-only solution.
Cortex also includes components for:
- Onboarding automation: New developers receive assigned accounts, secrets, and setup tasks through automated onboarding flows.
- Production-readiness checks: Production-readiness rules can be defined for services, APIs, and models, and these rules determine whether a service meets organizational thresholds before deployment.
- Software scaffolding: Developers can also generate new projects through templated scaffolding, which allows teams to maintain structure and consistency across services.
Pros:
- Centralized service catalog with ownership data.
- Automated onboarding sequences.
- Production-readiness rule enforcement.
- Template-based project generation.
Cons:
- Possible gaps in RBAC reporting, especially around temporary access or short-lived environments.
- Day-two operations, such as ephemeral environments and permission resets, may require additional configuration.
- Organizations with highly custom infrastructure may need extra work to align Cortex with existing internal standards.
- Heavy reliance on standardized templates may limit flexibility for teams that prefer custom setups.
Pricing: Custom quote.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
4.5 |
|
Developer friendliness |
3.8 |
|
Integrations |
4.0 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4.2 |
|
Support and resources |
3.9 |
|
Total |
4.08 |
8. CTO.ai: Developer-Centric DevOps Workflows
CTO.ai operates as a DevOps-as-a-Service platform built around event-driven workflows, containerized automation, and communication-based deployment triggers. Its goal is to streamline delivery without requiring teams to build or maintain a large internal platform.
The system uses a low-code model that blends ChatOps, GitOps, and Infrastructure as Code. This creates workflows that run through containers, CLI tools, and messaging channels like Slack.
CTO.ai includes several components centered on day-to-day development activity. Developers can generate instant preview environments for pull requests through containerized workflows.
Also, deployment triggers can be executed directly from Slack, which ties release steps to everyday communication tools. CTO.ai supports container-based command-line tasks that teams can incorporate into local or automated workflows.
Pros:
- Containerized workflows for automation.
- Slack-based deployment triggers.
- Event-driven workflow support.
- Low-code environment for building custom operations.
Cons:
- The low-code model may limit flexibility for large-scale or highly complex enterprise environments.
- Heavy reliance on Slack can be restrictive for organizations that use other communication platforms.
- Some teams may find the workflow structure too narrow if they require broader integrations or advanced customization.
- Preview environments and workflow containers may require tuning for organizations with detailed infrastructure policies.
Pricing: Starts at $3,500 per month, billed annually.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
4.0 |
|
Developer friendliness |
4.3 |
|
Integrations |
3.7 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
3.9 |
|
Support and resources |
4.1 |
|
Total |
4.0 |
9. Jira: Managing Complex, Cross-Team Projects at Scale
Jira is a long-standing work-tracking system created by Atlassian. It began as an issue and bug tracker for software teams and later expanded into a broader project-management environment through plugins, templates, and marketplace add-ons
Despite this expansion, its core structure still reflects its origins, which is why it remains centered on tasks, issues, stories, and epics rather than higher-level delivery metrics. The platform organizes work through boards, lists, timelines, and custom workflows that accommodate a wide range of team structures.
It is used across both small and large organizations for task planning and cross-team coordination. Jira’s roadmap features, dependency mapping, and collaborative editing tools give teams a structured way to map out project stages and keep track of related tasks.
Pros:
- Goal alignment features between tasks and company objectives.
- Dependency mapping across teams and projects.
- Real-time collaborative editing for shared task updates.
- Large marketplace for extensions.
Cons:
- Heavy configuration requirements, especially for teams seeking simple project management.
- Workflow customization can introduce administrative overhead.
- Originally built as an issue tracker, so some teams may find it less intuitive for strategic or high-level planning.
- Reliance on plugins for advanced features increases maintenance needs.
Pricing: Free tier available for up to 10 users.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
3.9 |
|
Developer friendliness |
3.7 |
|
Integrations |
4.5 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4.2 |
|
Support and resources |
4.0 |
|
Total |
4.06 |
10. GitLab: End-to-End DevSecOps and AI-Powered Delivery Pipelines
GitLab operates as an all-in-one DevSecOps platform that combines source control, CI/CD, security testing, and deployment management in a single system. It aims to reduce toolchain fragmentation by centralizing development, security, and delivery workflows.
The platform also incorporates AI features through GitLab Duo, which provides code suggestions, pipeline guidance, and lifecycle-level automation. GitLab includes several components built around secure software delivery.
Integrated security scanning runs during CI/CD and cloud-agnostic deployment options allow teams to deploy to various providers without being tied to one environment.
Pros:
- Integrated CI/CD, security, and deployment workflows.
- Cloud-agnostic deployment support.
- AI-assisted code and pipeline features.
- Unified DevSecOps environment.
Cons:
- Complex or highly customized workflows may require workaround steps or additional manual setup.
- A broad feature scope can introduce a learning curve for teams that prefer separate, specialized tools.
- AI coding features are less advanced than dedicated AI coding assistants.
- The platform’s all-in-one nature may limit flexibility for teams that want more modular configurations.
Pricing: Free tier for individuals, with pricing starting at $29 per user per month.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
4.5 |
|
Developer friendliness |
4.2 |
|
Integrations |
4.3 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4.0 |
|
Support and resources |
3.8 |
|
Total |
4.16 |
11. Datadog: Unified Monitoring Across Applications, Infrastructure, and Security
Datadog is an observability and security platform that collects data from applications, infrastructure, logs, and network components. It centralizes these signals into one environment so teams can review performance, trace issues across services, and monitor system behavior in real time.
The platform supports a wide range of integrations across cloud providers, databases, containers, and third-party services.
Datadog includes components such as:
- Continuous profiling for identifying resource-intensive code paths
- Synthetic monitoring for simulated user behavior
- Universal service monitoring for automatic service discovery
These functions operate across the platform’s broader monitoring stack, which brings together logs, metrics, traces, and security events.
Pros:
- Monitoring across infrastructure, applications, and security layers.
- Automatic service discovery.
- Synthetic tests for user-path simulation.
- Continuous profiler for runtime insight.
Cons:
- Cost escalates quickly when multiple modules (APM, logs, security, RUM, etc.) are enabled.
- High event volume can create alert fatigue if notification rules are not tuned.
- Storage and retention requirements may increase operational overhead.
- Broad feature scope introduces a learning curve for teams adopting it for the first time.
Pricing: Starts at $15 per host per month.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
4.2 |
|
Developer friendliness |
3.6 |
|
Integrations |
4.4 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4.1 |
|
Support and resources |
3.9 |
|
Total |
4.04 |
12. Typo: Developer Efficiency and Code-Quality Insights
Typo is a software engineering intelligence platform that unifies data from the software development lifecycle. Then it applies AI to identify workflow issues, code-quality risks, and delivery patterns.
Here’s how it works. Typo:
- Connects to a team’s development tools.
- Analyzes activity across repositories.
- Surfaces indicators related to delivery predictability, code churn, and team workload.
The platform includes predictive analytics to flag upcoming delays, as well as conversational check-ins that record developer sentiment and health trends.
Typo’s features revolve around:
- Forecasting sprint risks: Sprint-delay predictions rely on signals from ongoing tasks and story progression.
- Detecting code hotspots: Code-hotspot detection shows files or areas of a codebase with patterns of repeated changes or instability.
- Gathering developer feedback: Its developer check-ins provide qualitative data about satisfaction or stress levels, which some teams incorporate into discussions about workload or processes.
Pros:
- Predictive indicators for sprint delays.
- Code-hotspot analysis.
- Developer sentiment tracking.
- Integration across SDLC tools.
Cons:
- The platform is relatively new compared to long-established observability or DevOps tools.
- AI predictions may be less reliable in environments with large, multi-repository systems.
- Limited operational history in large enterprise contexts.
- Developer check-ins may introduce subjective data that varies widely between teams.
Pricing: Free tier available for up to 5 contributors.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
3.8 |
|
Developer friendliness |
4.1 |
|
Integrations |
3.7 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
3.9 |
|
Support and resources |
4.0 |
|
Total |
3.9 |
13. Faros AI: Enterprise-Scale Engineering Intelligence and Optimization
Faros AI is an engineering intelligence platform that aggregates data from SDLC tools, HR systems, financial sources, surveys, and internal workflows. Its goal is to create a unified operational view for organizations managing complex engineering environments.
The platform applies AI to analyze delivery patterns, operational signals, and workflow structures across teams.
Faros AI includes engineering benchmarking based on anonymized industry data, decision-support recommendations generated from real-time operational inputs, and lifecycle health monitoring that spans tools and repositories.
These components operate through a flexible ingestion layer that connects to many different data sources without requiring teams to significantly change their workflows.
Pros:
- Benchmarking against aggregated industry data.
- AI-driven decision support.
- SDLC health monitoring across tools.
- Flexible ingestion for diverse data sources.
Cons:
- Setup and customization typically require strong internal data engineering resources.
- Implementation can be time-consuming for organizations without existing data pipelines.
- The platform may be better suited for organizations with established operational maturity rather than small or rapidly growing teams.
- Broad data ingestion increases configuration work when connecting niche or proprietary systems.
Pricing: Custom quote.
|
Criterion |
Rating |
|
Metrics measurement |
4.1 |
|
Developer friendliness |
3.7 |
|
Integrations |
4.2 |
|
Data reliability and performance |
4.0 |
|
Support and resources |
3.8 |
|
Total |
3.96 |
DORA Metrics Measurement Challenges
You track DORA metrics for a reason, but the process can feel messy when the data isn’t clear or consistent. That confusion grows once different tools and workflows get involved. So, here are the main challenges you should keep in mind:
- Deployment frequency: One challenge is having multiple sources of deployment data across different environments, such as different teams, tools, or automated systems. All this can make it challenging to get a unified view of all deployments. Also, tracking the production environment is harder for on-premise apps or mobile apps because their deployments differ from cloud systems.
- Lead time for changes: The main challenge lies in standardizing the starting point, such as the first commit, and accounting for different Git workflows. Long-lived branches complicate tracking, while trunk-based development simplifies it.
- Change failure rate: Determining what qualifies as a failure and accurately tracking these incidents can be complex, especially if you don't have a standardized incident management system. Also, it's challenging to capture all incidents because they have many different sources to account for. And another challenge is attributing the failure to the correct deployment or team.
- Failed deployment recovery time: Accurately tracking recovery time can be complex due to incident severity and response efficiency variability. For accurate measurement, you need consistent incident reporting and management tools. Another challenge is having different incident sources to support.
How to Improve DORA Metrics
Improving your DORA metrics starts with strengthening your delivery pipeline: make it observable end-to-end, reduce friction in each stage, and create faster, safer recovery paths. Each metric points to a different part of that flow, so you need a clear plan for each one.
Here are the core areas that shape strong averages and the steps you can take to reach them.
1. Deployment Frequency
You deploy more frequently when your process is lightweight and repeatable. And this connects directly to what high-performing teams already show.
According to the 2025 State of AI-assisted Software Development report, 16.2% of elite teams deploy on demand, and 22.7% deploy once per hour to once per day. These numbers show how fast delivery becomes when the pipeline is clean.
How to improve deployment frequency:
- Break work into small chunks you can ship without fear.
- Set up a clear CI/CD path that always runs the same way.
- Remove manual approvals that slow you down unless they are required for compliance.
- Give your team a clear workflow so every change moves through the same steps.
- Keep your main branch healthy so you don’t pause work to fix merge issues.
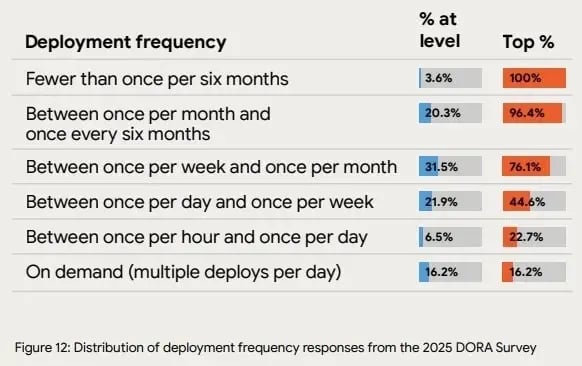
Image Source: 2025 State of AI-assisted Software Development report
2. Lead Time for Changes
Short lead time comes from steady flow. You reach that flow when code moves from idea to production without long waits between steps. And this aligns with what elite teams already do.
The 2025 State of AI-assisted Software Development report notes that 24.4% of top teams ship in under a day and 9.4% ship in under an hour. These numbers show how much speed depends on low friction in the handoff process.
How to improve lead time:
- Use clear tickets so you don’t lose time on unclear work.
- Limit work in progress to keep engineers focused.
- Remove slow review cycles.
- Reduce handoff delays by giving each team a set workflow.
- Automate build and test steps so nothing waits in the queue.
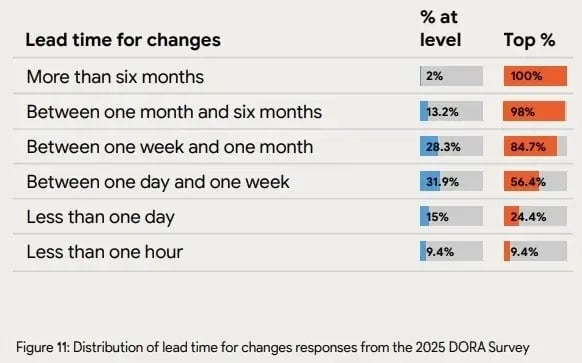
Image Source: 2025 State of AI-assisted Software Development report
3. Change Failure Rate
A lower change failure rate comes from steady testing and simple releases. And this is clear in the industry data.
The 2025 State of AI-assisted Software Development report shows elite teams holding 8.5% of changes in the 0-2% failure band and 16.7% in the 2-4% band. These numbers show how stable releases get when issues surface early.
How to improve your change failure rate:
- Add automated tests that run on every pull request.
- Keep feature flags ready so you can turn off risky code fast.
- Use trunk-based development to avoid long-lived branches.
- Run lightweight checks early instead of large batches right before the release.
- Fix flaky tests so they don’t hide real issues.

Image Source: 2025 State of AI-assisted Software Development report
4. Failed Deployment Recovery Time
Fast recovery is the result of strong observability and easy rollback paths. And the 2025 State of AI-assisted Software Development report shows 21.3% recovering in under an hour and 56.5% recovering in under a day. These numbers show how good visibility and simple rollback steps reduce downtime.
How to improve recovery time:
- Keep rollback steps simple so anyone can trigger them.
- Add clear alerts for both failures and early warning signs.
- Use playbooks so your team knows the first steps to take.
- Keep logs, traces, and metrics easy to reach.
- Test your rollback or restore steps frequently so they don’t fail during real incidents.
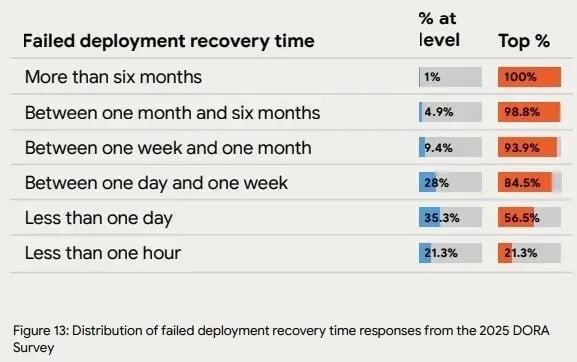
Image Source: 2025 State of AI-assisted Software Development report
Look Beyond DORA Metrics
If you've read this far, you know the best DORA metrics tools. Each platform has its pros and cons, though, so choose wisely.
Of course, DORA metrics aren't the only metrics that count.
Your team may also need to follow Agile metrics, like daily sprints, or you may want to track team morale.
In that case, Axify offers solutions for different teams and stakeholders.
If you're a CIO, use Axify's new executive dashboard to gain a high-level view of engineering performance and make informed decisions to drive strategic improvements. If you're a software project manager, Axify is excellent for monitoring real-time project progress and team health. That's how you can maintain both product delivery and team wellbeing.
While DORA metrics provide critical insights into your team's DevOps performance, you need to integrate them with other key performance indicators and holistic metrics.
That's the best way to better understand your team's effectiveness and health and to work toward your business goals.
Book a virtual tour today and see how Axify can help.






.png?width=60&name=About%20Us%20-%20Axify%20(2).png)



